Book Appointment Now
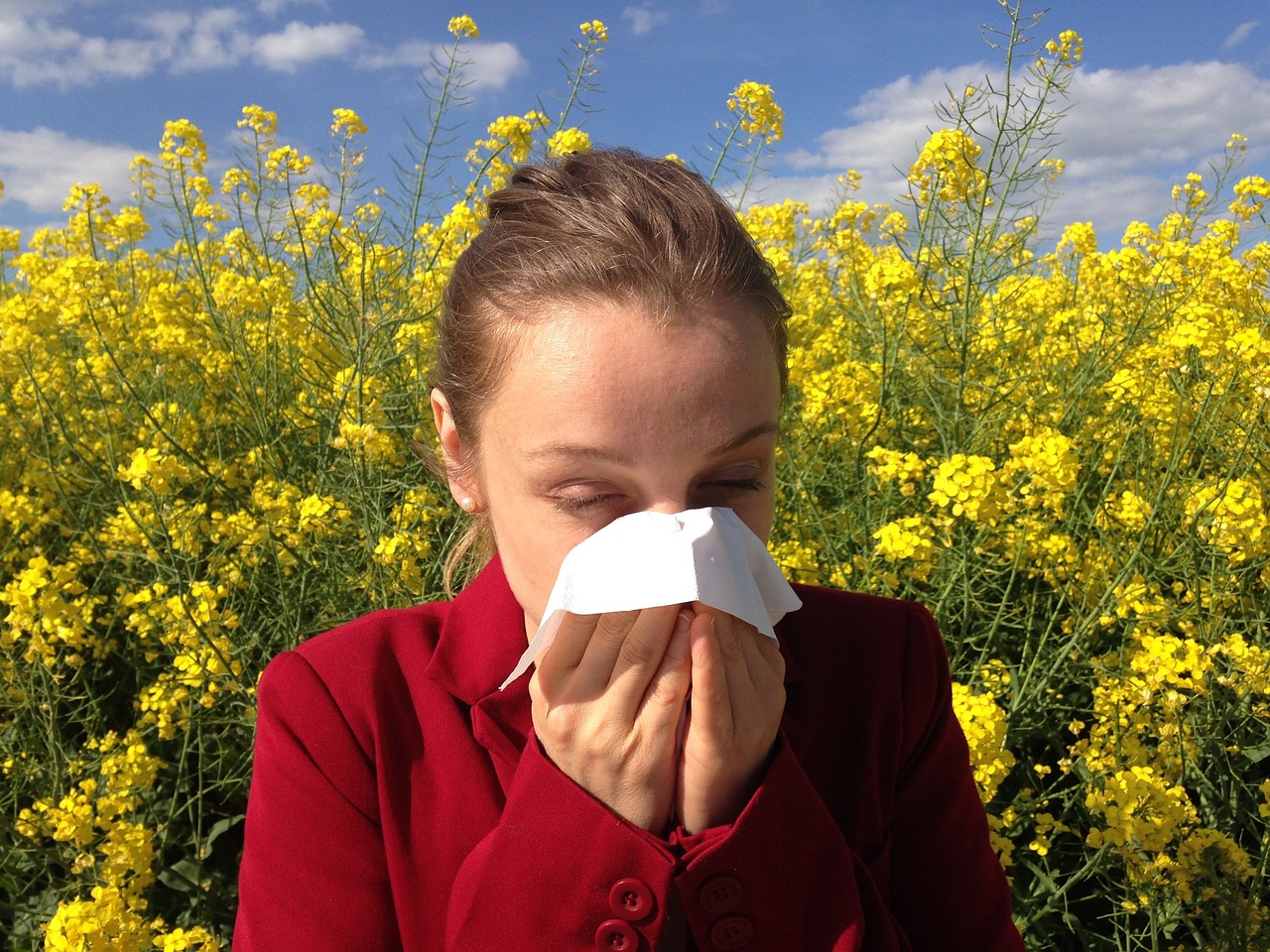

Causes and Prophylactics of Allergies in Young Children
Allergies in young children are a growing concern in pediatric nursing. With an increasing number of children being diagnosed with various forms of allergies, such as food allergies, respiratory allergies, and skin conditions, understanding their causes and how to prevent them is critical. In the context of midwife, neonatal, and pediatric nursing, early detection and management are essential to safeguarding children’s health. This article explores the causes and prophylactics of allergies in young children, offering insight into best practices for healthcare professionals.
Do you need nursing paper writing help regarding causes and prophylactics of allergies assignment? ![]()
Causes of Allergies in Young Children
Allergies occur when the immune system reacts to harmless substances, considering them harmful. In young children, common allergens include certain foods, pollen, animal dander, and dust mites.
Genetic Predisposition to Allergies
A significant factor contributing to allergies in children is their genetic makeup. Children born to parents with a history of allergies are more likely to develop allergic conditions. In pediatric nursing, it is important to assess family history during routine check-ups to identify potential risks.
- Food Allergies: Milk, eggs, peanuts, and tree nuts are the most common food allergens in children.
- Environmental Allergies: Pollen, mold, pet dander, and dust mites are frequent triggers, especially for neonatal and pediatric patients.
- Skin Conditions: Eczema and contact dermatitis often have an allergic component.
Immature Immune Systems
Young children, particularly infants and newborns, have immature immune systems, making them more susceptible to allergies. Midwives and neonatal nurses need to educate parents on how to reduce exposure to allergens during this critical stage of development.
Prophylactics of Allergies in Young Children
Prevention is key in managing allergies in children. Nurses in the midwife, neonatal, and pediatric fields play a crucial role in educating parents and implementing preventive measures. See also Maternal Child Care of Nursing.
Breastfeeding and Immunity Building
Breastfeeding provides essential nutrients and antibodies that help strengthen a baby’s immune system. In fact, exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months is recommended to reduce the risk of food allergies.
- Promotes gut health, reducing the likelihood of allergies.
- Provides antibodies that protect against infections and allergens.
Introducing Allergenic Foods Early
Recent studies suggest that introducing allergenic foods like peanuts, eggs, and dairy products during infancy can lower the risk of allergies. In pediatric nursing, educating parents on the importance of this early exposure under medical supervision is vital.
Environmental Control Measures
Limiting exposure to environmental allergens can significantly reduce the risk of allergies in young children. Simple steps such as keeping homes free from dust mites, using hypoallergenic bedding, and regularly vacuuming can help.
- Keeping pets out of the bedroom to reduce dander exposure.
- Using air purifiers to lower pollen and dust concentrations indoors.
Role of Pediatric Nurses in Allergy Prevention
Pediatric nurses are at the forefront of managing and preventing allergies in young children. They provide crucial education, early interventions, and support to parents.
Early Screening and Diagnosis
Early screening for allergic reactions can help in the timely diagnosis and management of allergies. Nurses should encourage parents to report any signs of allergic reactions, such as rashes, swelling, or breathing difficulties.
Educating Parents and Caregivers
Providing information on both the causes and prophylactics of allergies helps parents make informed decisions. Educational resources, such as pamphlets and counseling sessions, are effective tools for nurses.
Understanding the causes and prophylactics of allergies in young children is essential for healthcare professionals, especially those in midwife, neonatal, and pediatric nursing. By recognizing genetic predispositions, promoting breastfeeding, and implementing environmental control measures, nurses can play a critical role in the prevention and management of allergies in children. Early intervention and ongoing education are crucial in ensuring a healthier future for young patients.